
Patients with Type I and Type II diabetes are susceptible to diabetic retinopathy, a common consequence of diabetes mellitus. The development of this illness is closely linked to the length of the disease and inadequate glycemic control. In the first phase, it causes the blood vessels in your retina to expand; eventually, the blood vessels occlude.
At Barman Eye Care Centre, our best eye specialists in Gurgaon are committed to providing the best eye care and support to individuals with diabetic retinopathy.

Diabetic Retinopathy: Risk factors, Complications, and Prevention
Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy can start with no symptoms at all. As the illness worsens, the following symptoms appear:
- Fuzzy vision
Vision changes, causing floating specks to appear
- Blind areas
- Modifications to color perception
- Unexpected loss of vision
- Dual perception
- Eye pain in more severe situations
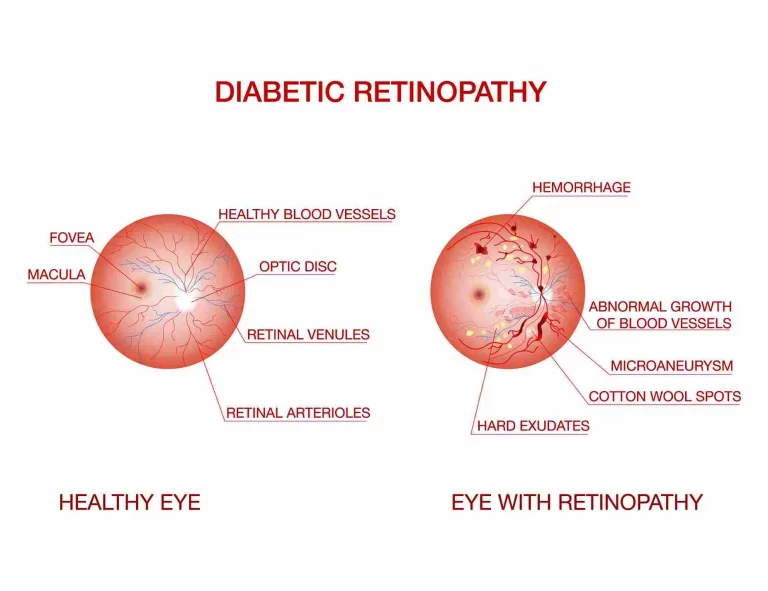
The development of microaneurysms may be the first indication of diabetic retinopathy that your doctor notices. These are little red dots in the back of the eye that are balloon-shaped outpouchings of microscopic blood vessels in the retina. They can occasionally shatter, impairing vision and causing bleeding from the retina into the vitreous gel that fills the eye.
Proliferative diabetic retinopathy is a more severe kind of diabetic retinopathy that can leave scars that impair vision. New blood vessels develop over the retina and into the vitreous in proliferative retinopathy. There’s a chance that these blood vessels break, resulting in eye injury and hemorrhage. Although the blood can sometimes be reabsorbed, total blindness can result from the retina detaching.
Similar to diabetic retinopathy, hypertensive retinopathy may not exhibit any symptoms in the early stages. But when the illness worsens, symptoms include:
- headaches, changes in vision
- abrupt blindness in one or both eyes
- dual perception
Causes of Diabetic retinopathy
It can strike anyone with diabetes. Deterioration of the blood artery network that supplies the retina with nutrition is the primary cause of diabetic retinopathy. Elevated blood glucose levels weaken, damage, or develop abnormally in the arteries, which limits blood supply to the retina.
It is more common in people who have:
- Inadequate management of glucose levels
- Being pregnant
- Blood pressure
- elevated cholesterol
- People who smoke
- extended period of diabetes
Diagnosis for Diabetic Retinopathy
Your ophthalmologist can identify it during a thorough, dilated eye exam. A thorough diabetic eye examination consists of the following:
- Testing visual acuity: This exam gauges how well you can see at different distances.
- Tonometry: Your doctor will use this test to measure the intraocular pressure.
- Pupil dilation: The eye care specialist will apply drops to enlarge or dilate the pupil. This makes it possible for the ophthalmologist to assess the retina and optic nerve.
- OCT-angiography and optical coherence tomography (OCT): This method uses light waves to take finely detailed pictures of the retinal tissue. It offers a thorough examination of the vascularity and structure of the retina.
When severe diabetic retinopathy is present, a fluorescein angiography is performed to check for blood leaks or damage.
Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy
Taking care of the retinopathies’ underlying causes is essential to their treatment.
For those with diabetes, lowering blood sugar levels is essential to postponing the development of diabetic retinopathy. In addition to adhering to a nutritious diet and exercise regimen, proper management of diabetes entails taking prescribed medications, such as insulin or other diabetes medications.
Controlling blood pressure can help avoid hypertensive retinopathy. Complications can be avoided by taking the right drugs to lower and raise blood pressure. A healthy diet, regular exercise, and different lifestyle modifications like giving up smoking will significantly reduce the incidence of retinopathy.
Laser treatment and intraocular drug injections (e.g., corticosteroids and vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors) manage diabetic retinopathy. Your doctor can suggest a vitrectomy if there has been scarring or if a blood vessel has bled into the vitreous. This treatment can restore lost vision or maintain it by removing a portion of the vitreous and any scar tissue that may be present. Retinal reattachment may need surgery if retinal detachment has occurred.
Hypertensive retinopathy is treated with blood pressure-lowering drugs. For this illness, prevention is essential.
See your doctor before beginning any vigorous exercise if you have proliferative retinopathy.
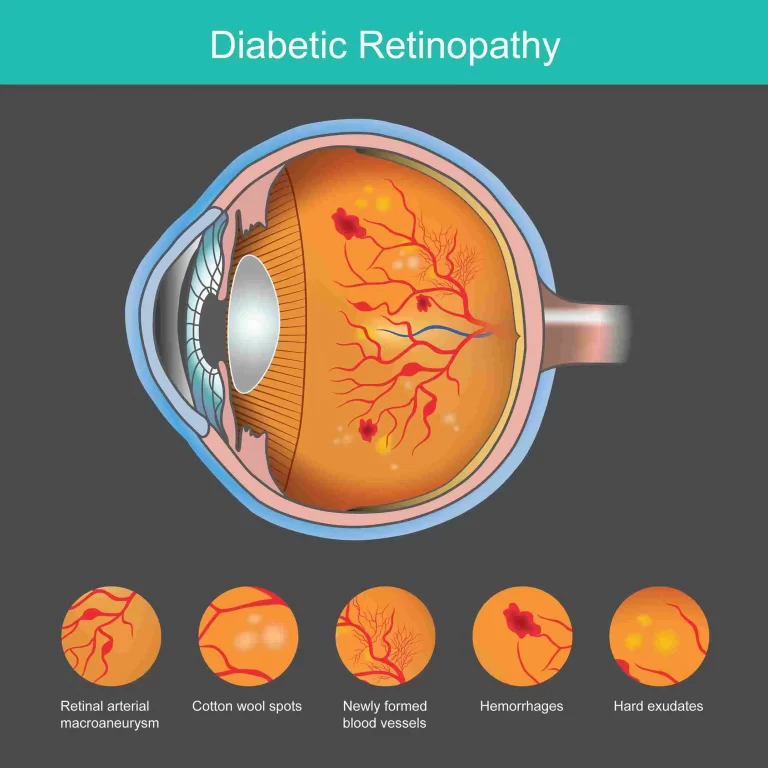
Surgery of Diabetic Retinopathy
The procedure known as a vitrectomy is used to treat diabetic retinopathy. When laser therapy is not successful or the condition is too advanced for the laser to stabilize clinically, a vitrectomy is carried out. During this process, we remove the cloudy vitreous gel inside the eyeball while the patient is under local anesthesia. After that, a transparent liquid or gas takes its place. Additionally, any scar tissue pulling on the vitreous blood or retina is removed.
Precautions for Diabetic Retinopathy
Managing blood sugar levels is the most significant and controllable risk factor in developing diabetic retinopathy. This will aid in delaying the condition’s progression when combined with better blood pressure and cholesterol control and quitting smoking. To lessen the likelihood of recurrent eye bleeding, it is advised to refrain from lifting large objects for the next two weeks after laser therapy.
Risks
Unmonitored diabetic retinopathy and uncontrolled diabetes can cause glaucoma, abrupt sight loss, and a painful blind eye.
Restoration
After surgery for the ailment, recovery might take a few weeks or many months. Depending on the patient’s initial clinical state at presentation Compared to individuals with more severe disease or retinal detachments, patients with a less advanced version of the disease have a significantly more noticeable improvement in their eyesight.
CONCLUSION
Diabetic retinopathy is a very severe complication of diabetes that may lead to vision loss and other eye-related problems. It often starts with no noticeable symptoms, making regular eye exams crucial for those with diabetes. Controlling blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol prevents its progression. Treatment options like laser therapy, injections, and surgery can help manage the condition, but early intervention is critical. The risks of uncontrolled diabetic retinopathy are glaucoma and sudden vision loss, underscoring the importance of proactive management. Recovery after surgery varies but is generally better with early diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatments is essential for preserving vision and improving the quality of life for individuals with diabetes. At Barman Eye Care Centre, which stands amongst the best eye hospitals in Gurgaon, we are genuinely committed to providing the best eye care and support to individuals with diabetic retinopathy.
